84
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 77-91
Mao
et al.
,
The runoff variation characteristics of Dongting Lake in China
•
ISSN 2007-2422
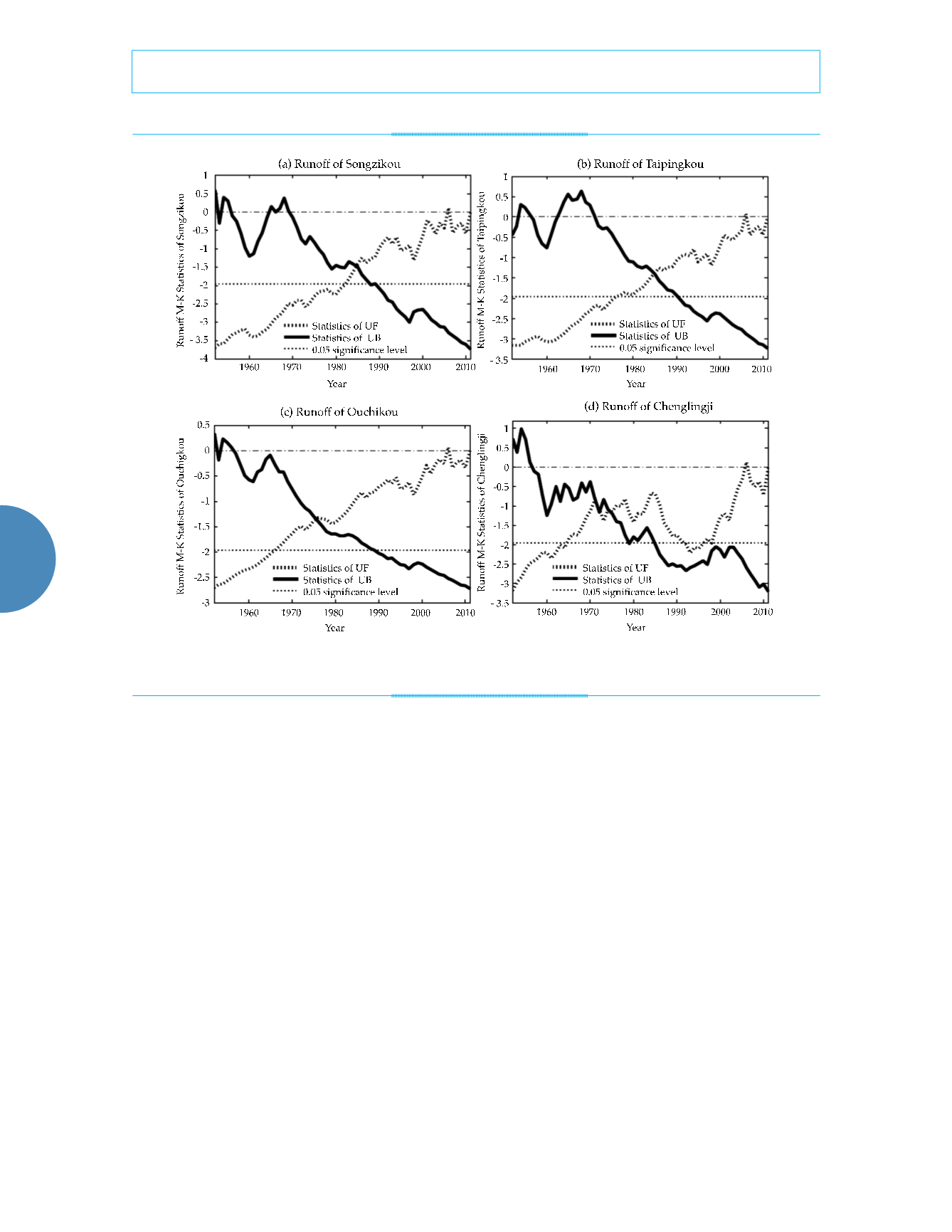
Songzikou’s runoff in figure 4(a) presents
that UF and UB intersected in 1985 within the
confidential intervals. After the mutation, UF
overcame the confidential threshold to form a
significant change. It demonstrated that after
continuous descending, its runoff experienced
an obvious and sudden change in the vicinity
of 1985 which was exactly the 4
th
year after the
completion of Gezhou Water Control Project.
The discharge kept on decaying after the muta-
tion point. Taipingkou’s runoff in figure 4 (b)
mutated at the same time with that of Songzikou
and broke the confidential threshold in 1990
downwardly. The mutation time of Ouchikou’s
runoff was earlier and it’s UF and UB met
between 1975 and 1976 within the confidential
zone. Its UF breaks the confidential zone and
exhibited a significant attenuation trend in 1989.
Ouchikou’s runoff was affected by the lower-
Jingjiang River’s channel straightening project
from 1967 to 1972. Figure 4 (d) shows outflow of
Dongting Lake mutated between 1974 and 1975,
after which the outflow revealed a continuous
and downward oscillation and intersected with
the confidential line in 1985 showing a signifi-
cant attenuation.
In order to identify the accuracy of M-K mu-
tation test, this paper uses the mean-difference
T-test to verify the accuracy of the mutation
year. The results are shown in table 3.
According to results from mean-difference
T-test, statistic t value of three bayous and
Chenglingji is 6.533, 7.660, 10.156 and 4.366,
respectively. All have passed the significant test
(significant level
α
= 0.01, the critical value is
2.704). Four rivers’ runoff did not mutate which
means they have failed to pass the significant
test.
Figure 4. The M-K trend analysis of runoff of three outflows and Chenglingji.


