82
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 77-91
Mao
et al.
,
The runoff variation characteristics of Dongting Lake in China
•
ISSN 2007-2422
the flood-inducing system of Dongting Lake
and then made a conclusion as follows (Zeng,
Hao, & Liu, 2004): The meteorology system in
the upper reach leads to the flood. Watersheds
of four rivers were in the same monsoon zone
whose rain season is fromMay to August. Rain
belt moved from upper reach to downstream
or even cover the whole watershed. When four
river’s flood arrived at the bank of Dongting
Lake, it was experiencing its rainy period. The
internal and external floods coincided to form
severe disasters. The most typical examples are
floods of Taojiang and Taoyuan in 1995 and
1996.
Inter annual runoff variability
Inter annual runoff variations are commonly
calculated by variation coefficient (
C
v
) and
inter annual extreme ratio.
C
v
is the ratio of the
standard deviation and arithmetic mean of the
sample sequence. It is an important indicator
to reflect the evenness of inter annual runoff.
Results are in table 2. According to calculation
results, the
C
v
of inflow and outflow is between
0.194-0.761, among which three bayous’
C
v
are
larger than others’. Results demonstrate the
variability and unstable status of inter annual
runoff.
C
v
of three bayous is different from that
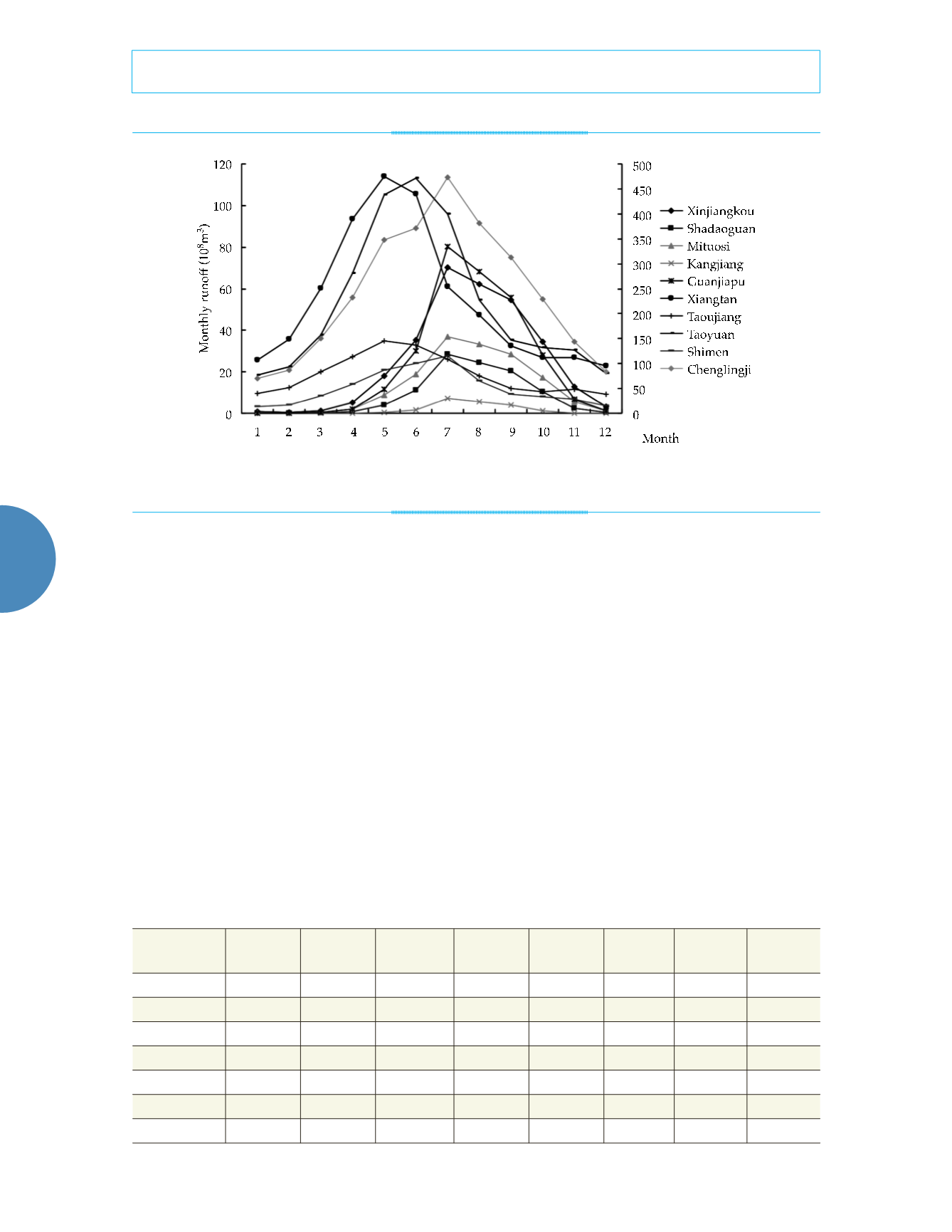
Figure 2. Monthly distribution characteristics of main rivers’ runoff in Dongting Lake.
Table 2. Average and variation coefficient of rivers in Dongting Lake basin.
Hydrological
station
Statistic
years
Annual
mean Maximum Year
Minimum Year
Cv
Extreme
ratio
Xiangtan
1951-2011
654
1 035
1994
281
1963
0.251
0.73
Taojiang
1951-2011
227
372
1954
103
1956
0.229
0.72
Taoyuan
1951-2011
636
1 030
1954
379
2011
0.194
0.63
Shimen
1951-2011
146
264
1954
83
1992
0.277
0.69
Songzikou 1951-2011
409
750
1954
119
2006
0.272
0.84
Taipinkou
1951-2011
155
270
1954
34
2006
0.333
0.87
Ouchikou
1951-2011
333
1 156
1954
29.12
2006
0.761
0.97


