80
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 77-91
Mao
et al.
,
The runoff variation characteristics of Dongting Lake in China
•
ISSN 2007-2422
and vertical component of the synthetic vector
respectively;
W
is the annual runoff.
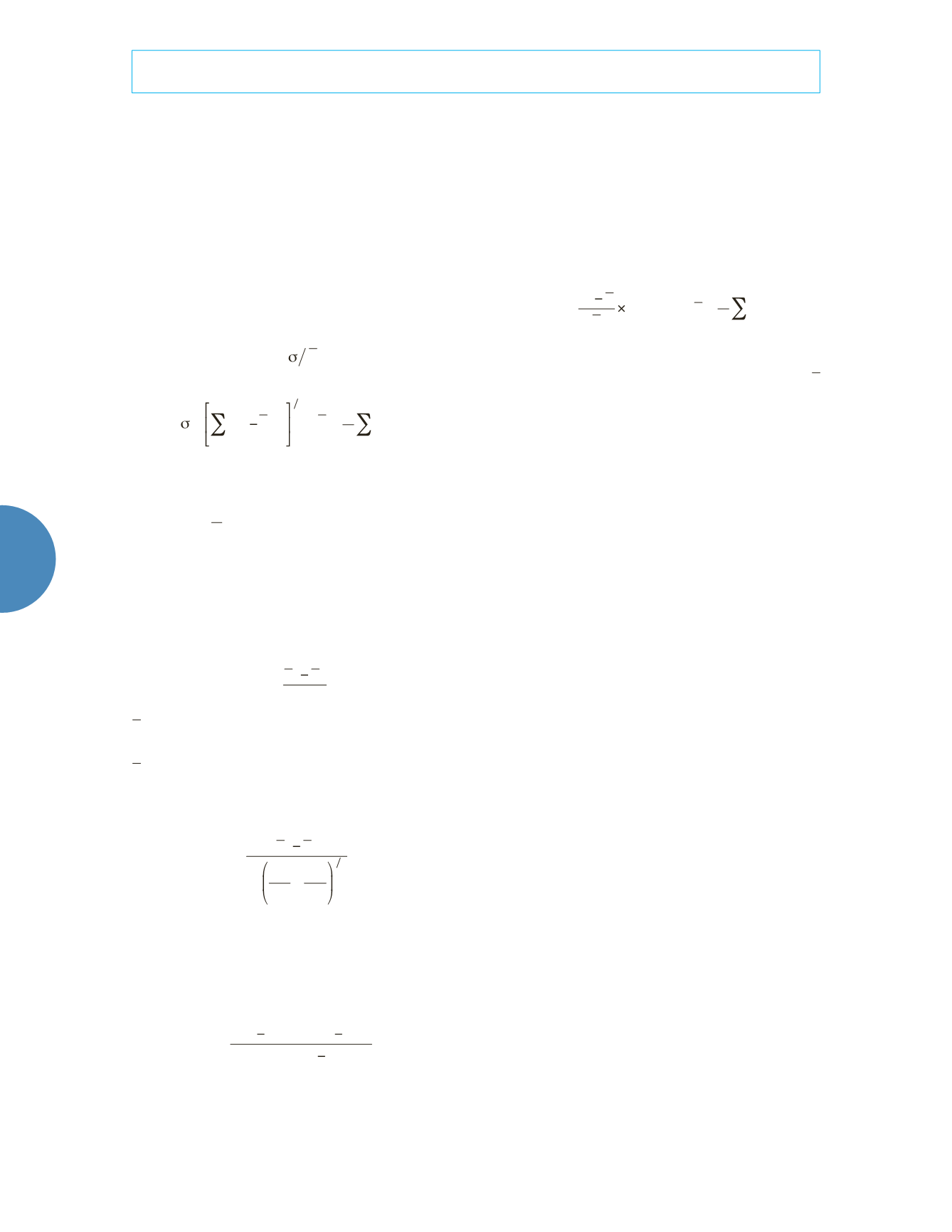
Annual distribution uniformity coefficient
Annual distribution uniformity coefficient re-
flects annual runoff distribution uneven degree
in a watershed (Li, Li, & Wang, 2002; Yao, Guan,
& Gao, 2003; Huang, 2003). Calculation formula:
C
v
=
R
(5)
=
R
i
R
i
(
)
2
i
=
1
n
1 2
R
=
1
n
i
R
i
=
1
n
(
i
=1, 2, …, 12)
(6)
C
v
represents annual distribution uniformity
coefficient;
R
represents average monthly run-
off;
R
i
represents monthly runoff.
The mean difference T test
Defined mutation index of a sample sequence:
AI
j
=
x
1
x
2
s
1
+
s
2
(7)
x
1
,
s
2
stand for the mean value and standard
deviation before the base year m respectively;
x
2
,
s
2
stand for the mean value and standard
deviation after the base year
m
respectively.
Defined the statistics:
t
=
x
1
x
2
s
p
1
m
1
+
1
m
2
1 2
(8)
m
1
,
m
2
represent the sample length of the two
sequence before and after base year
m
respec-
tively;
s
p
stands for joint sample variance:
s
p
2
=
(
m
1
1)
s
1
2
+
(
m
2
1)
s
2
2
m
1
+
m
2
2
(9)
Given a certain significant level
a
(
a
= 0.05),
when
t
>
t
a
, the mean value of
m
1
and
m
2
on
both sides of the reference point has a significant
difference, namely a mutation happen in the
reference point.
Anomaly percentage
Calculation formula:
K
i
=
x
i
x
x
100% ;
x
=
1
n x
i
i
=
1
n
(10)
K
i
represents the anomaly percentage of the
i
year;
x
i
represents the runoff of the
i
year;
x
stands for mathematical expectation of
n
annual
runoff,
i
= 1, 2, 3,…,
n
;
n
represents the total
number of samples.
Runoff characteristics of Dongting Lake
Essential characteristics of Dongting Lake’s
inflow and outflow
The complicated flood combination of Dongting
Lake’s inflow is composed of three bayous and
four rivers. The flood of three bayous is similar
to Yangtze River whose flood peaks are obesity
and last long. The distribution of three bayous’
runoff is uneven, water in flood season (May to
October) accounts for over 90% of the total. Four
rivers’ flood peak is sharp, thin and last shorter.
Floods in flood season contribute 65% to the
total. According to the measured hydrological
data from 1951 to 2011, incoming water from
three bayous and four rivers is 2 567 × 10
8
m
3
/a,
and outflow was 2 862 × 10
8
m
3
/a. water came
from three bayous of Yangtze Rivers was 912 ×
10
8
m
3
/a, accounts for 31.9% of the total outflow.
Four rivers contribute 1 655 × 10
8
m
3
/a in the
discharge which is 57.8% of the total. The rest
local inflow is 295 × 10
8
m
3
/a, occupying 10.3%
of the portion.
Annual runoff variation characteristics
Concentration degree and Concentration period
is a vector approach which was first applied to
the analysis of meteorological factors. In 1982,
Tang introduced this method to identified the


