100
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 93-103
Song & Song,
Kinetics and influential factors of nanoscale iron-facilitated nitrate-nitrogen removal
•
ISSN 2007-2422
the
Ea
included the total amount of reduced
nitrate and oxidized nanoscale iron. Since the
activation energy of the reaction, which was
primarily influenced by the mass transfer of the
aqueous solution, was limited to 10-20 kJ/mol,
the factor that primarily influenced the reaction
was the mass transfer of the solution rather
than the chemical reactions (Liou
et al
., 2005).
These results corresponded with those reported
by Liou, who used a nanoscale iron to remove
nitrate-nitrogen at 10-60 ºC (Liou
et al
., 2005).
Product analysis of the nitrate-nitrogen
removal process
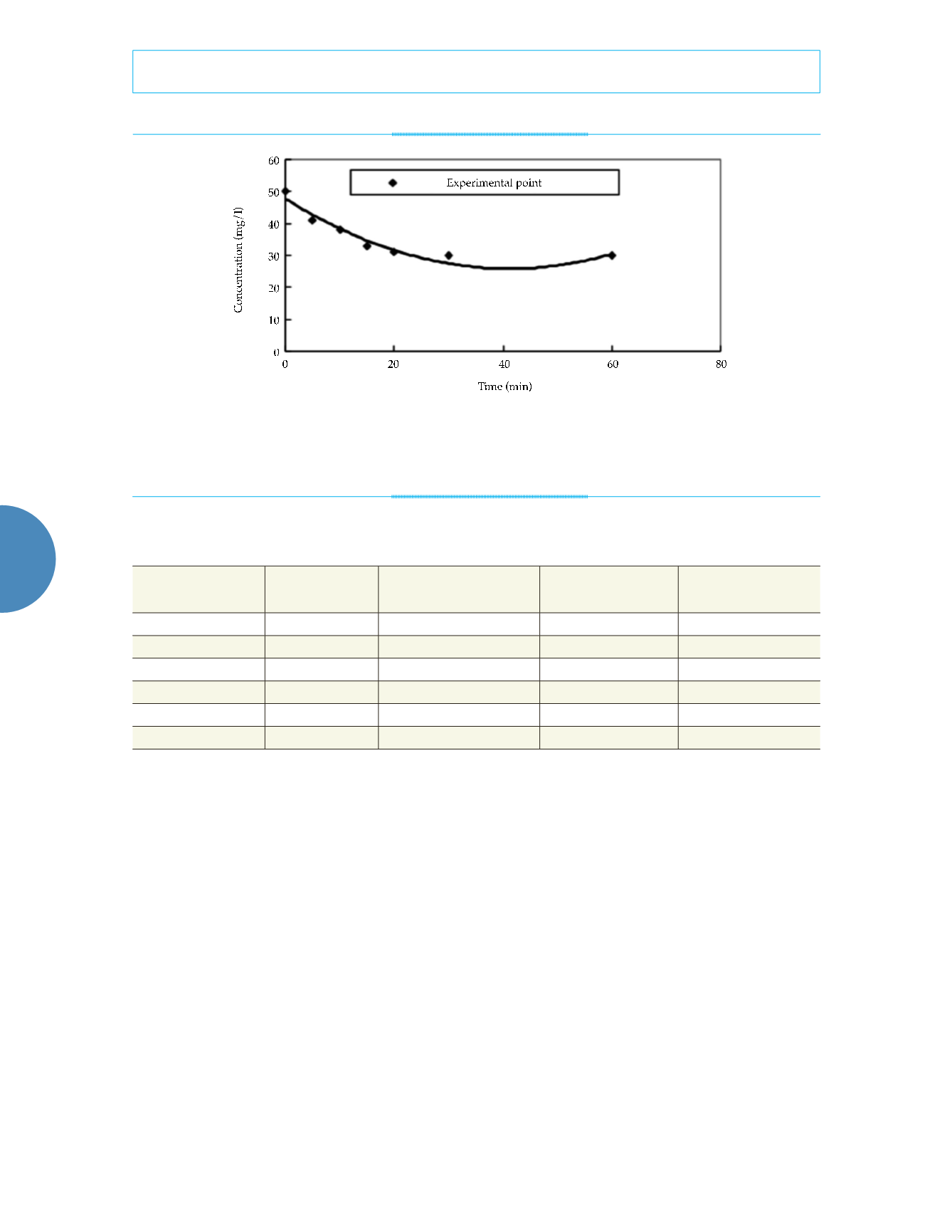
At a constant temperature and pH of 25 ºC and
7.0, respectively, 0.5 g of nanoscale iron was
added to water containing 50 mg/l of nitrate
nitrogen in order to determine the nitrate ni-
trogen, nitrite nitrogen, and ammonia concen-
trations of the solution after different reaction
times. The results are shown in figure 7. As
shown in figure 7, chemical reactions occurred
during the nanoscale iron-facilitated removal
of the nitrate-nitrogen. The nitrite content was
very low. According to the curves of the three
nitrogenous compounds, the reactant concentra-
tion decreased from the initial concentration of
50 to 45 mg/l, indicating that a portion of the
nitrate nitrogen was converted into nitrogen
and then released.
According to the experimental results,
during the reaction between the nitrate nitro-
gen and nanoscale iron, most of the nitrate
Figure 5. Kinetics analysis of experimental data according to pseudo-second-order at 25 ˚C
(the following pseudo-second-order kinetic equation was used to describe the reaction between the nitrate nitrogen and
nanoscale iron:
C
t
=
C
0
-
k
t
C
2
a
/ 1 +
k
t
C
a
).
Table 1. Reaction rate constant at different temperatures.
Temperature
(ºC)
k (mg/(l·min))
Correlation coefficient
(
r
)
Mean square error
(MSE)
Mean absolute error
(MAE)
25
0.008
0.9901
3.0532
1.2078
30
0.009
0.9894
1.7475
1.5564
35
0.010
0.9849
2.7315
1.4972
40
0.011
0.9818
3.2267
1.6060
45
0.012
0.9861
3.0446
1.4689
50
0.014
0.9966
0.7865
0.7078


