98
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 93-103
Song & Song,
Kinetics and influential factors of nanoscale iron-facilitated nitrate-nitrogen removal
•
ISSN 2007-2422
results are shown in figure 4. As shown in this
figure, the nitrate nitrogen content varied at dif-
ferent temperatures, with nitrate removal rates
of 50 and 60% at 25 °C and 50 °C, respectively.
Thus, as the temperature increased, the amount
of nitrate nitrogen removed by the nanoscale
iron increased. However, these effects were not
significant. Thus, efficient nitrate-nitrogen re-
moval can be achieved at various temperatures
in practical engineering applications. Figure
4 also shows that the reaction rate decreased
gradually over time, but became constant after
approximately 10 minutes. Therefore, the reac-
tion that occurred between the nanoscale iron
and nitrate nitrogen cannot be determined with
this information alone. However, the products
of the reaction between the nanoscale iron and
water as well as the conditions of the aqueous
solution determined the products of nitrate
reduction. Thus, the reaction that occurred be-
tween the nanoscale iron and nitrate nitrogen
under different conditions can be described by
the following equation:
NO
3
-
+ 6H
2
O + 8 е
-
→
NH
3
+ 9OH
-
(5)
Since the removal of nitrate-nitrogen occurs
via adsorption and reduction facilitated by
both the large specific surface area and high
activity of nanoscale iron, the reaction between
nitrate nitrogen and nanoscale iron cannot be
effectively described by an adsorption reaction
equation alone. Previous studies concerning
the kinetics of nanoscale iron-facilitated nitrate-
nitrogen removal have yielded varying results.
Liou (Liou
et al
., 2005) reported that the reaction
between nanoscale iron and nitrate nitrogen can
be described with a pseudo-first-order kinetic
equation. In contrast, Gordon (Molly
et al
., 2003)
claimed that this reaction cannot be described
by a pseudo-first-order kinetic equation or
first-order kinetic equation. Since the effects of
adsorption and reduction and interrelationships
on nanoscale iron-facilitated nitrate-nitrogen
removal cannot be determined, the products
and reactant concentrations are assumed to be
influenced by the conditions under which the
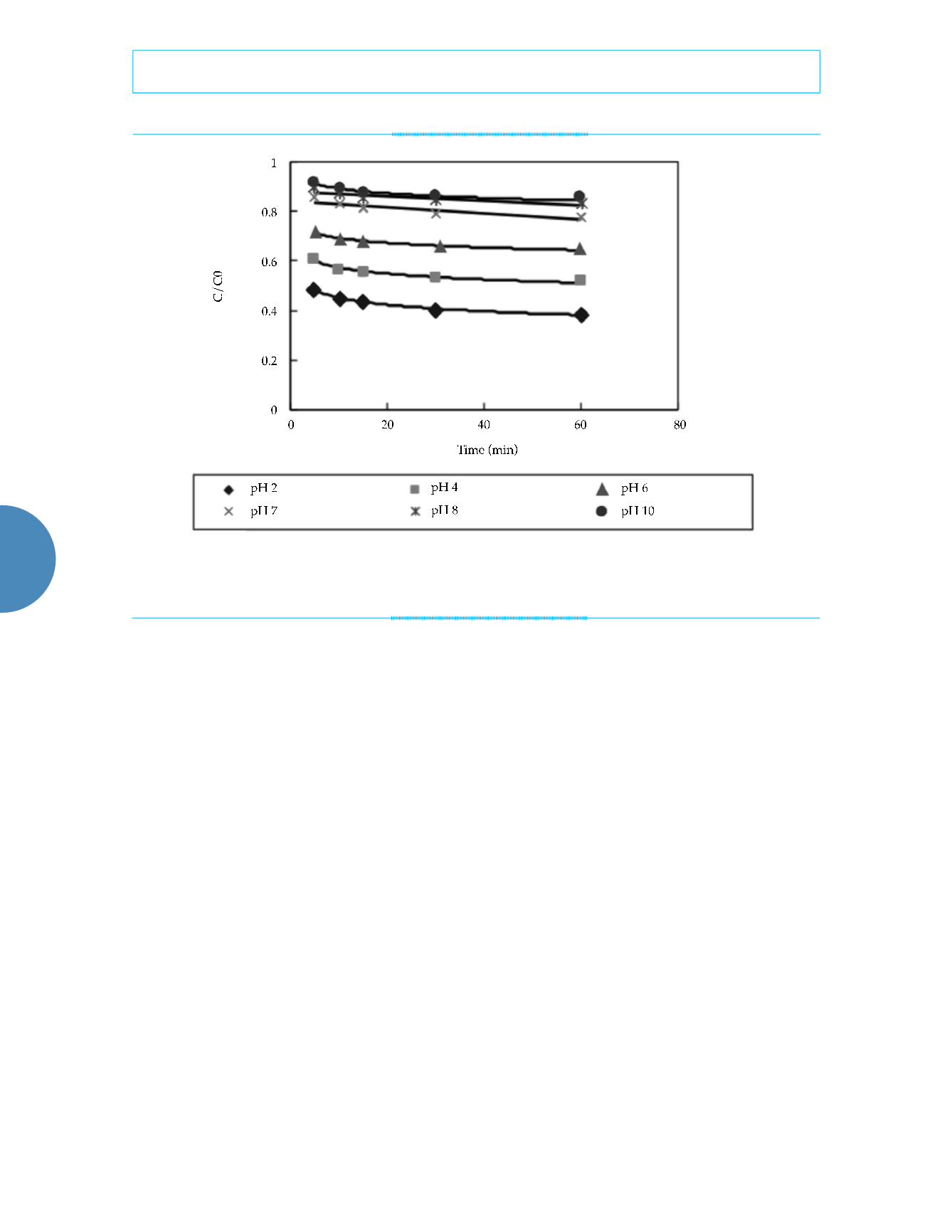
Figure 3. Influence of different pH values on removal efficiency (in the experiment, 0.5 g of nanoscale iron was added to water
containing 50 mg/l of nitrate nitrogen at a constant temperature of 25 °C).


