53
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 51-60
Kan
et al.
,
Daily streamflow simulation based on improved machine learning method
ISSN 2007-2422
•
PKEK model
PKEK model is an improved version of the
previously proposed PEK model. It is proposed
for the purposed of improving the non-linear
simulation capability of the PEK model. It is
combined by the PMI-based input variable
selection (IVS) module, the
K
-means clustering
algorithm based input variable clustering mod-
ule, and the ENN and KNN simulation mod-
ule. The PKEK model can be seen as a hybrid
approximator which composed by a
K
-means
clustering module and multiple PEK modules.
The simulation and calibration method of the
PKEK model is as follows: The input variables
are selected by the PMI-based separate IVS
scheme to generate the selected input vectors.
After that, each selected input vector is fed into
the
K
-means clustering algorithm to determine
which category it belongs to. After that, for each
selected input vector, we choose a correspond-
ing PEK module to calculate the output. In the
PEK module, the output is estimated by the
ENN, and the output error is estimated by the
KNN regression. The final simulated output
is the sum of the estimated output and output
error. The calibration of the PKEK approximator
is almost the same with the PEK approximator.
The difference is that the
K
-means algorithm
needs to be calibrated by an iterative method
(Grigorios &Aristidis, 2014; Kapageridis, 2015).
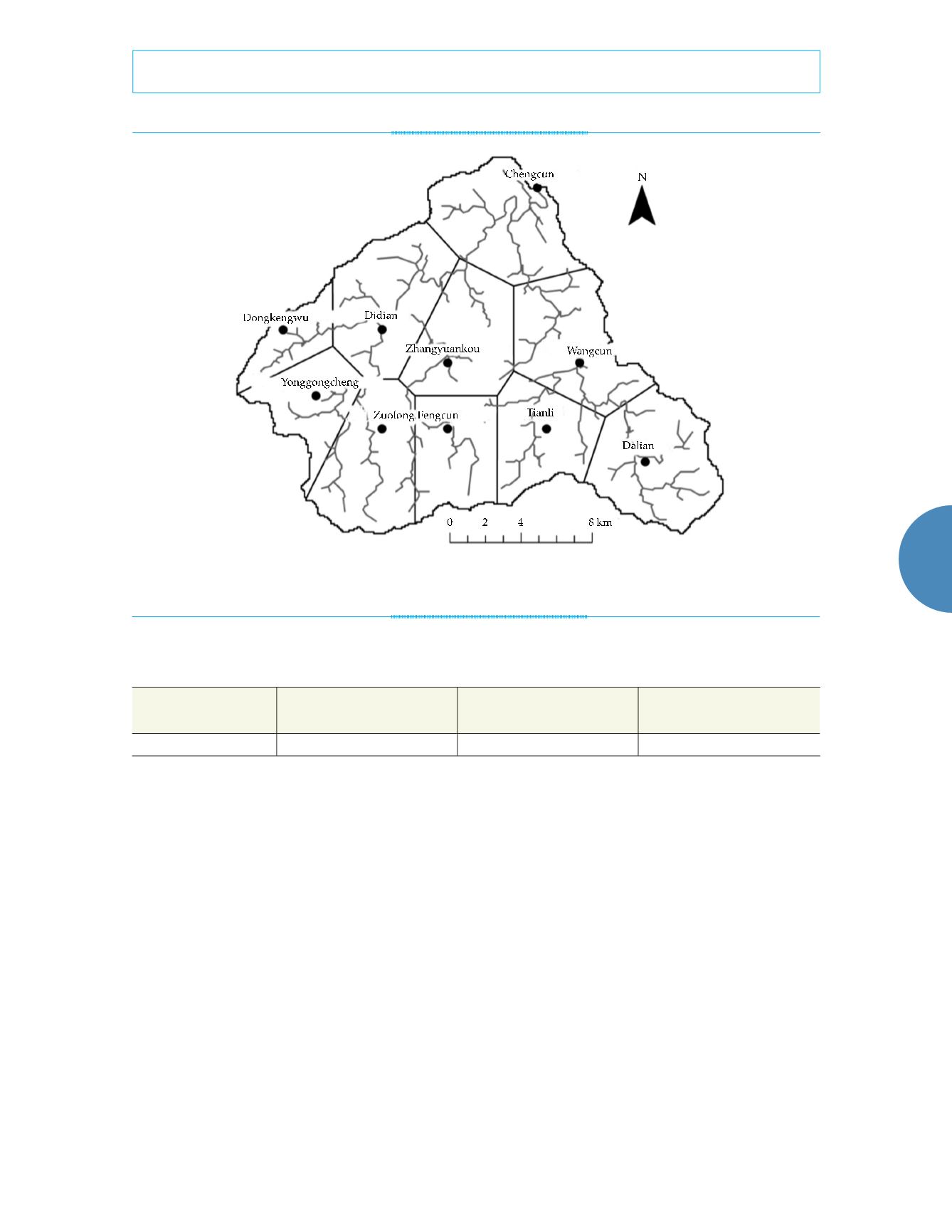
Figure 1. Watershed map for the Chengcun catchment.
Table 1. The hydrological and meteorological characteristics of the Chengcun catchment.
Area
(km
2
)
Annual mean
rainfall (mm)
Annual mean
evapotranspiration (mm)
Annual mean
streamflow (m
3
/s)
290
1 600
730.9
5 440.9


