23
Tecnología y Ciencias del Agua
, vol. VIII, núm. 2, marzo-abril de 2017, pp. 19-30
Fan
et al
.
, Effect of drip irrigation with saline water on the shelterbelts to soil and groundwater environment in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert, China
ISSN 2007-2422
•
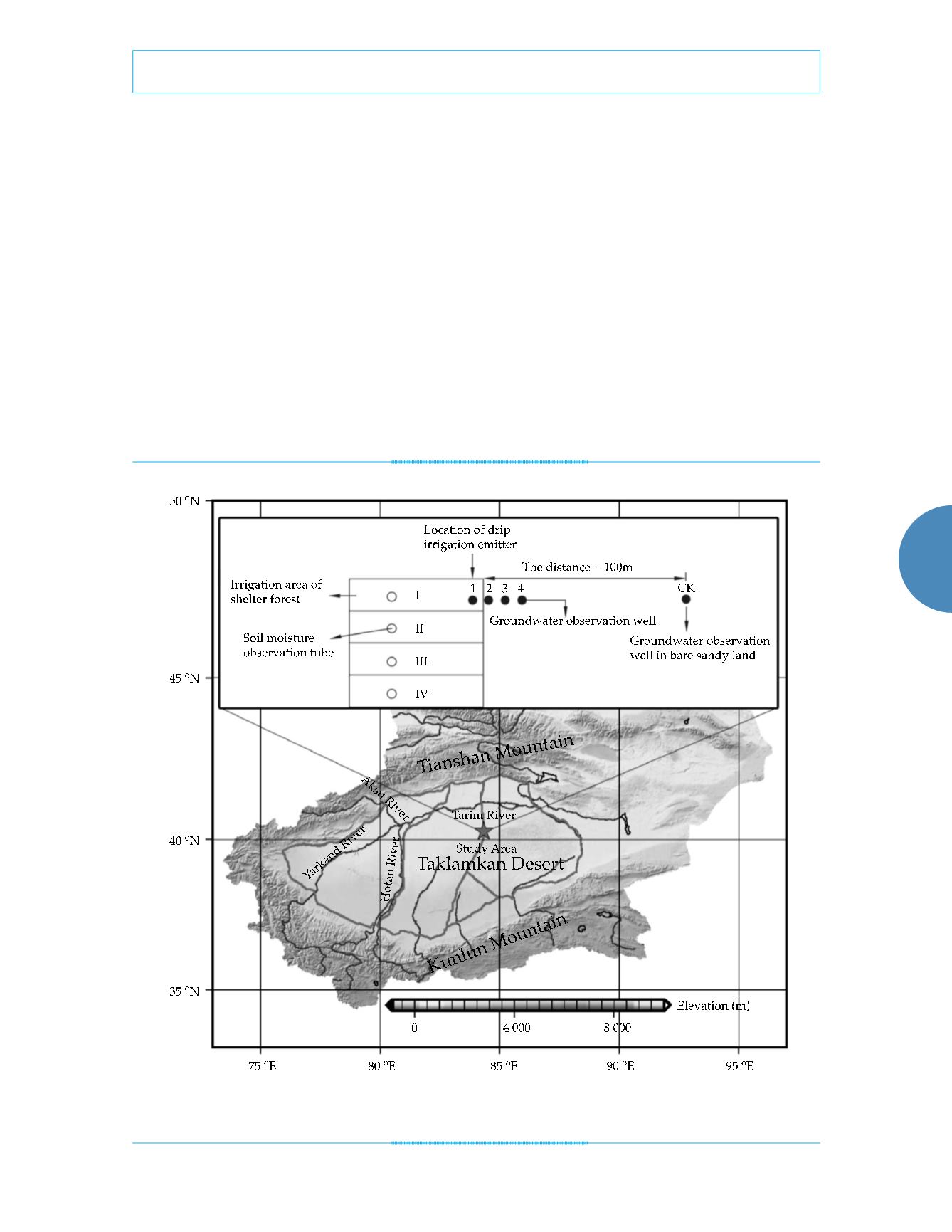
In each experimental area, a 2 m long Soil
moisture observation tube was embedded into
soil under emittter made of aluminum/plastic
composite pipe of 50 mm in diameter. Soil mois-
ture was determined via neutron probes (Gard-
ner & Kirkham, 1952) with five replicates after
irrigation, then the mean value of replications
was used as the soil water content. This rapid,
in situ
, nondestructive means of measuring soil
moisture profiles in forestry (Wells & Fityus,
2011) was used in this work to determine soil
moisture at 10-cm intervals from the soil surface
to a depth of 180 cm.
Results and discussion
Spatial distribution of soil water and salt
under different irrigation conditions
Water spatial distribution
Four different irrigation cycle experiments
during irrigation season were carried out in
four different regions of well irrigation area
(table 1). According to figure 2, after the irriga-
tion, the soil water content in region I with the
original irrigation system reached saturation at
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental layout.


