15
Referencias bibliográficas
Areco, M. M., Hanela, S., Duran, J., & dos Santos Afonso, M. (2012). Biosorption of Cu(II),
Zn(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) by dead biomasses of green alga Ulva lactuca and the development of a
sustainable matrix for adsorption implementation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 213-214, 123–
132. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.073
Das, B. K., Roy, A., Koschorreck, M., Mandal, S. M., Wendt-Potthoff, K., & Bhattacharya, J.
(2009). Occurrence and role of algae and fungi in acid mine drainage environment with special
reference to metals and sulfate immobilization. Water Research, 43(4), 883–894.
doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.046
Mayes, W. M., Batty, L. C., Younger, P. L., Jarvis, A. P., Kõiv, M., Vohla, C., & Mander, U.
(2009). Wetland treatment at extremes of pH: A review. Science of The Total Environment,
407(13), 3944–3957. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.045
Sheoran, A. S., & Sheoran, V. (2006). Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in
wetlands:
A
critical
review.
Minerals
Engineering,
19(2),
105–116.
doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2005.08.006
Anexos
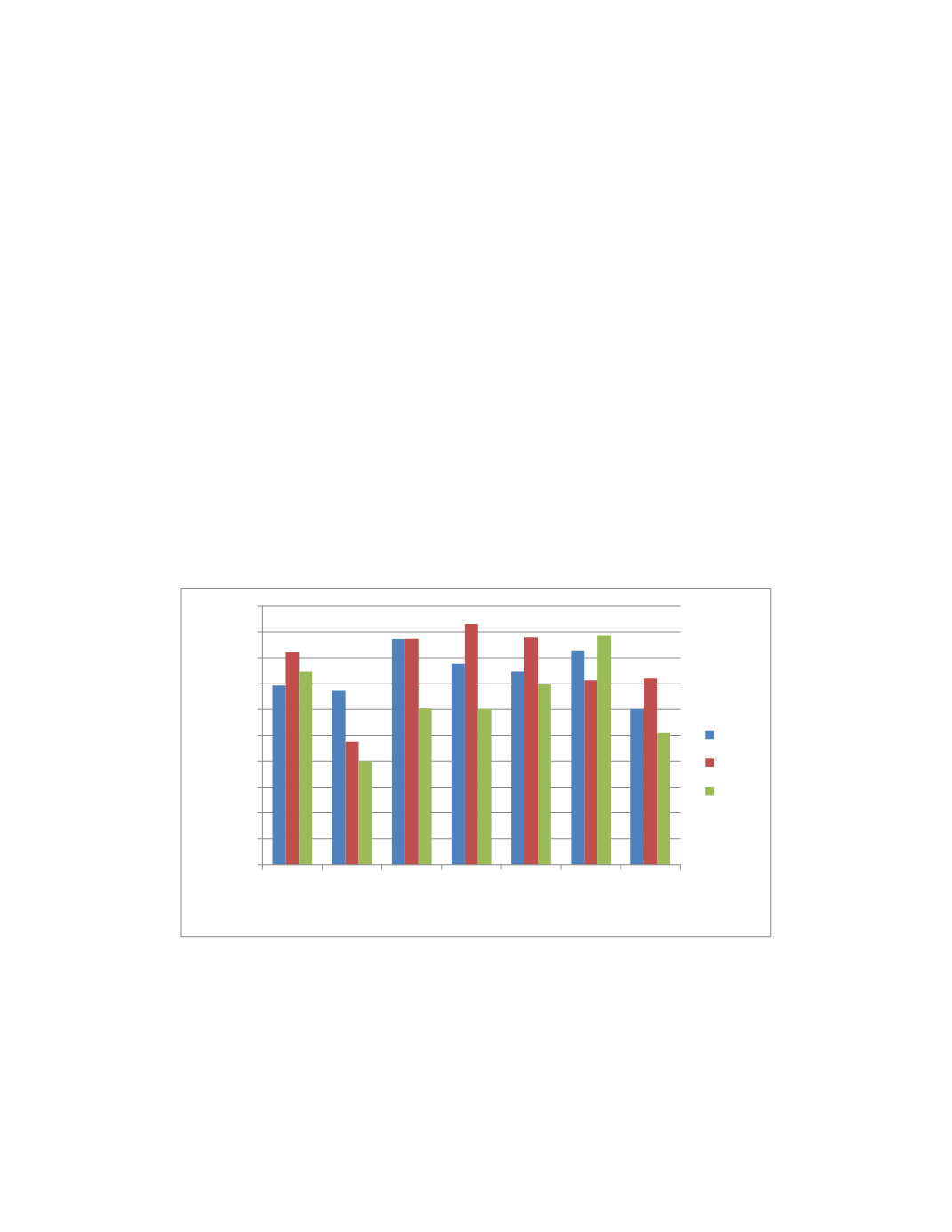
Figura 1. Porcentajes de remoción promedio para el plomo en cada fase vs. Tipos de sistemas
evaluados en el estudio.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
HFSSH+P HFSSH HFS+P HFS+A HFS HFV+P HFV
% Remoción para Plomo
Tipos de sistemas evaluados
fase 1
fase2
fase3


